Notifications
6 minutes, 22 seconds
-88 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews

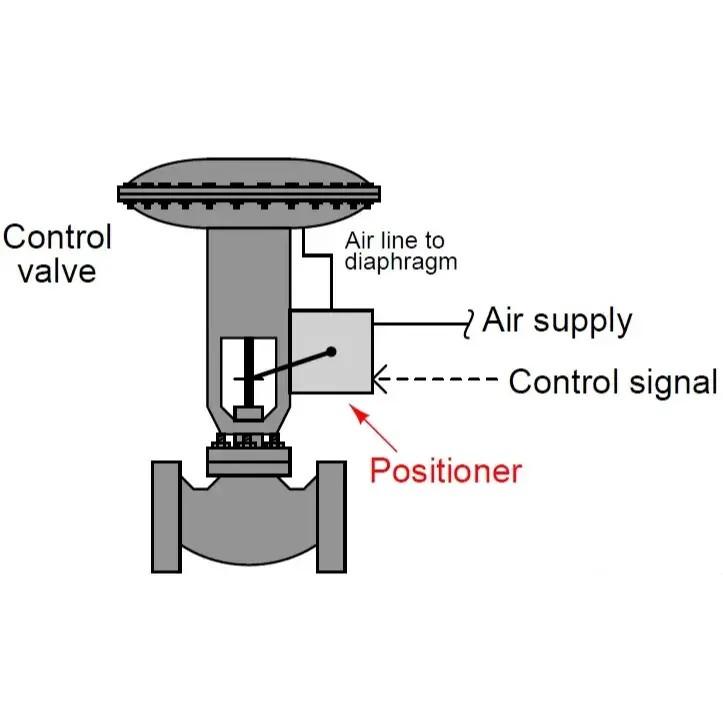
A control valve positioner is an essential device that ensures the precise movement of the valve stem in response to a control signal. It plays a critical role in maintaining accurate valve positioning, enabling optimal flow control in various industrial processes. Below are the primary components of a control valve positioner and their respective functions:
The positioner receives an input signal from the process controller, which indicates the desired position of the valve stem. This signal could be in various forms depending on the type of positioner and system:
Pneumatic Signal: Typically in the range of 3-15 psi, commonly used in older or more traditional systems.
Electric Signal: Often a 4-20 mA current signal, used in more modern systems with electric actuators.
Digital Signal: In some advanced systems, digital protocols like HART or Fieldbus may be used for more precise control.
This mechanism continuously monitors the actual position of the valve stem. The feedback is crucial for ensuring that the valve stem's position aligns with the desired position indicated by the input signal. Common feedback systems include:
Mechanical Linkage: A direct mechanical connection between the valve stem and the positioner, usually via a spring and lever system.
Non-contact Sensors: More advanced feedback systems use electronic sensors such as Hall effect or optical sensors for precise measurement without physical contact.
This component is responsible for adjusting the actuator to align the valve position with the control signal. It works in response to the feedback and control signals, which allow the valve to be positioned accurately within its travel limits. The actuating mechanism typically involves pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic systems.
The control element manages the supply of energy (whether pneumatic, electric, or digital) to the actuator. It regulates how much energy is needed to move the valve stem to the correct position based on the feedback received. This element is critical for translating the input signal into mechanical action that adjusts the valve.
The operation of a control valve positioner is driven by the need to accurately position the valve in real time, in line with the desired process parameters. The working principle involves a continuous cycle of receiving signals, comparing positions, adjusting signals, and making corrections to achieve and maintain the correct valve position. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how the positioner works:
The positioner first receives a control signal from the process controller. This signal tells the positioner what the desired valve position should be. The signal might be pneumatic, electric, or digital, depending on the system configuration.
The positioner compares the desired position (setpoint) with the actual position of the valve stem. This comparison is made using a feedback mechanism, which continuously monitors the valve's position. The feedback mechanism could be a mechanical linkage (e.g., a spring) or an electronic sensor providing real-time data to the positioner.
If the desired position does not match the actual position, the positioner calculates the discrepancy. Based on this difference, it generates a corrective signal that instructs the actuator to adjust the valve stem's position.
The actuator responds to the corrective signal by moving the valve stem to the correct position. The actuator may be powered by pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic energy, depending on the system design. This action is intended to minimize the difference between the setpoint and the actual position of the valve.
The positioner continually adjusts the actuator as necessary to bring the actual valve position in line with the desired position. Once the desired position is achieved, the positioner and actuator maintain the valve in this position, continuously checking for any deviations that might require further adjustments. The system remains in equilibrium until a new control signal is received, which initiates the process again.
Control valve positioners are vital for ensuring the accurate and precise operation of control valves in industrial systems. By receiving the control signal, comparing the desired and actual positions, and making continuous adjustments to the actuator, positioners help maintain optimal flow control in the system. Their ability to provide real-time feedback and corrections ensures smooth operation, enhances system efficiency, and reduces the risk of control issues or process instability.
If you’re interested in learning more or discussing specific needs, Control Valves Manufacturer would be happy to assist you. Feel free to reach out, and they’ll provide the expert guidance and solutions you’re looking for!

