Notifications
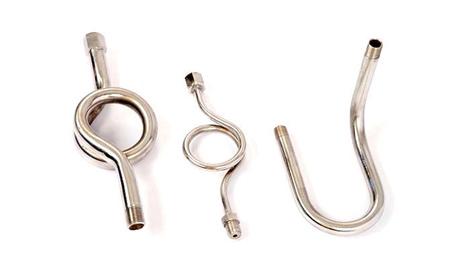
10 minutes, 15 seconds
-273 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews
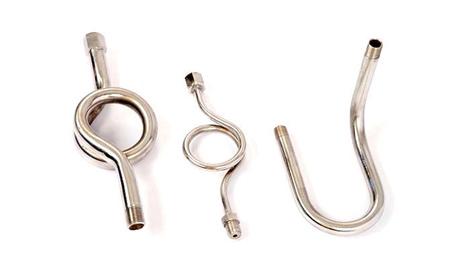
Syphon pipes are a fascinating part of fluid mechanics, widely used in both domestic and industrial settings. These pipes work on the simple yet powerful concept of gravity and atmospheric pressure, allowing liquids to transfer from a higher level to a lower one without the need for pumps or additional energy sources. Their efficiency and simplicity have made them an indispensable tool for various applications. In this blog, we’ll explore everything you need to know about syphon pipes how they work, the different types, their uses, and the numerous benefits they offer.
A syphon pipe is a tube that allows the transfer of liquids using the syphon effect. The syphon effect occurs when a liquid is drawn from one container to another due to a difference in pressure. This difference in pressure causes the liquid to move from an elevated source to a lower discharge point without the use of pumps or electrical devices. The process is initiated by first filling the syphon pipe with the liquid, and once the flow begins, it continues automatically until the liquid source is depleted.
Syphon pipes are commonly used for applications that require liquid to be transferred over short to medium distances without the need for power. Their simple design and reliable operation make them an excellent solution for a variety of fluid transfer needs.
Understanding the basic working principle behind syphon pipes is crucial to appreciating their function. Here’s how they operate:
Initiating the Syphon: The process begins by filling the syphon pipe with the liquid. If the pipe is not full, air pressure will interfere with the flow, preventing the syphon effect from occurring.
Atmospheric Pressure: Once the pipe is filled with liquid, the difference in atmospheric pressure at both ends of the pipe becomes key. The liquid in the pipe at the elevated end is subjected to higher pressure than the liquid at the discharge point, which is at a lower pressure.
Flow Continuation: Once the liquid starts flowing, gravity pulls it down from the high point to the low point. As long as the pipe is immersed in the liquid and there is no airlock, the flow will continue automatically, driven by the pressure difference.
End of Flow: The syphon will stop once the liquid level in the source container drops below the intake end of the syphon pipe. At this point, air enters the pipe, breaking the syphon action and halting the flow.
There are several types of syphon pipes, each designed for specific purposes. Below are some of the most commonly used types:
Straight Syphon Pipe: This is the simplest form of syphon, consisting of a straight tube with one end submerged in the liquid and the other positioned to drain the liquid to a lower level. It’s efficient for short distances and small-scale applications.
U-Bend Syphon Pipe: This syphon pipe features a U-shaped bend that allows for more control over the liquid flow. It is often used when the distance between the source and the discharge point is longer or when there is a need to adjust the flow rate.
Overflow Syphon Pipe: Commonly used in water management systems, the overflow syphon is designed to carry excess liquid from one container to another, ensuring that the container does not overflow. It’s often used in reservoirs or water tanks.
Vacuum Syphon Pipe: This type of syphon pipe uses a vacuum pump to initiate the flow of liquid. It is typically used in industrial settings where high-efficiency fluid transfer is required.
Siphon with Non-Return Valve: This syphon pipe includes a non-return valve, which prevents the reverse flow of liquid. This feature is especially important in systems where backflow can cause contamination or damage.
Syphon pipes have a wide range of applications across different sectors. Some of their most common uses include:
Wastewater and Sewage Systems: Syphon pipes are often used in sewage and wastewater treatment systems, where they help transfer liquid waste from one area to another, especially when there is no electricity to power pumps.
Aquariums: In aquariums, syphon pipes help perform water changes by draining water from the tank and refilling it. They are also useful for cleaning debris from the substrate.
Irrigation: In agriculture, syphon pipes are used to transport water across fields. They are particularly useful in regions with limited access to electricity, as they rely on gravity for fluid movement.
Brewing and Winemaking: In brewing and winemaking, syphon pipes help transfer liquids between containers during the fermentation process. This ensures that the liquids are not exposed to air, preserving their quality.
Fuel Transfer: Syphon pipes are commonly used to transfer fuel from one container to another. This method is popular in situations where the use of pumps is impractical or too costly.
Syphon pipes offer several advantages, which is why they are widely used in various industries. Here are some of their key benefits:
Energy Efficiency: One of the main benefits of syphon pipes is that they require no external power. They rely entirely on gravity and atmospheric pressure, making them an energy-efficient solution for fluid transfer.
Simplicity and Cost-Effectiveness: Syphon pipes are easy to install and operate. Their simplicity reduces the need for complicated setups, making them a low-cost option for fluid transfer in many applications.
Low Maintenance: Once the syphon pipe is installed, it generally requires little to no maintenance. There are no moving parts that can break down, and as long as the pipe is kept free of blockages, it will continue to work effectively.
Eco-Friendly: Syphon pipes do not require electricity, making them an environmentally friendly choice. They are a sustainable way to move liquids without contributing to carbon emissions or energy consumption.
Versatility: Whether in residential, commercial, or industrial settings, syphon pipes are versatile and can be used in various applications, from wastewater treatment to agricultural irrigation.
While syphon pipes are simple to use, it’s important to keep a few factors in mind during installation to ensure they work effectively:
Material Selection: Choose the right material for your syphon pipe based on the liquid being transferred. Materials like PVC, copper, or stainless steel are commonly used due to their durability and resistance to corrosion.
Pipe Size: The diameter of the syphon pipe affects the flow rate. A larger pipe will allow for more liquid to flow through it at a faster rate, while a smaller pipe may slow down the transfer.
Elevation: The greater the difference in height between the intake and discharge ends of the syphon, the faster the liquid will flow. Ensure the pipe is installed in a way that maximizes this pressure difference.
Airlocks: Airlocks can interrupt the flow of liquid through the syphon pipe. To avoid this, ensure that the pipe is fully submerged and free from any air pockets.
Syphon pipes are a simple yet highly effective solution for transferring liquids from one place to another. Their energy efficiency, low maintenance, and versatility make them ideal for a wide range of applications, from residential water systems to industrial fluid management. Whether you're using them for irrigation, wastewater management, or even aquarium maintenance, syphon pipes offer a reliable, cost-effective method of fluid transfer.
syphon pipes syphon pipe types syphon pipe uses how syphon pipes work benefits of syphon pipes

