Notifications
8 minutes, 28 seconds
-27 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews

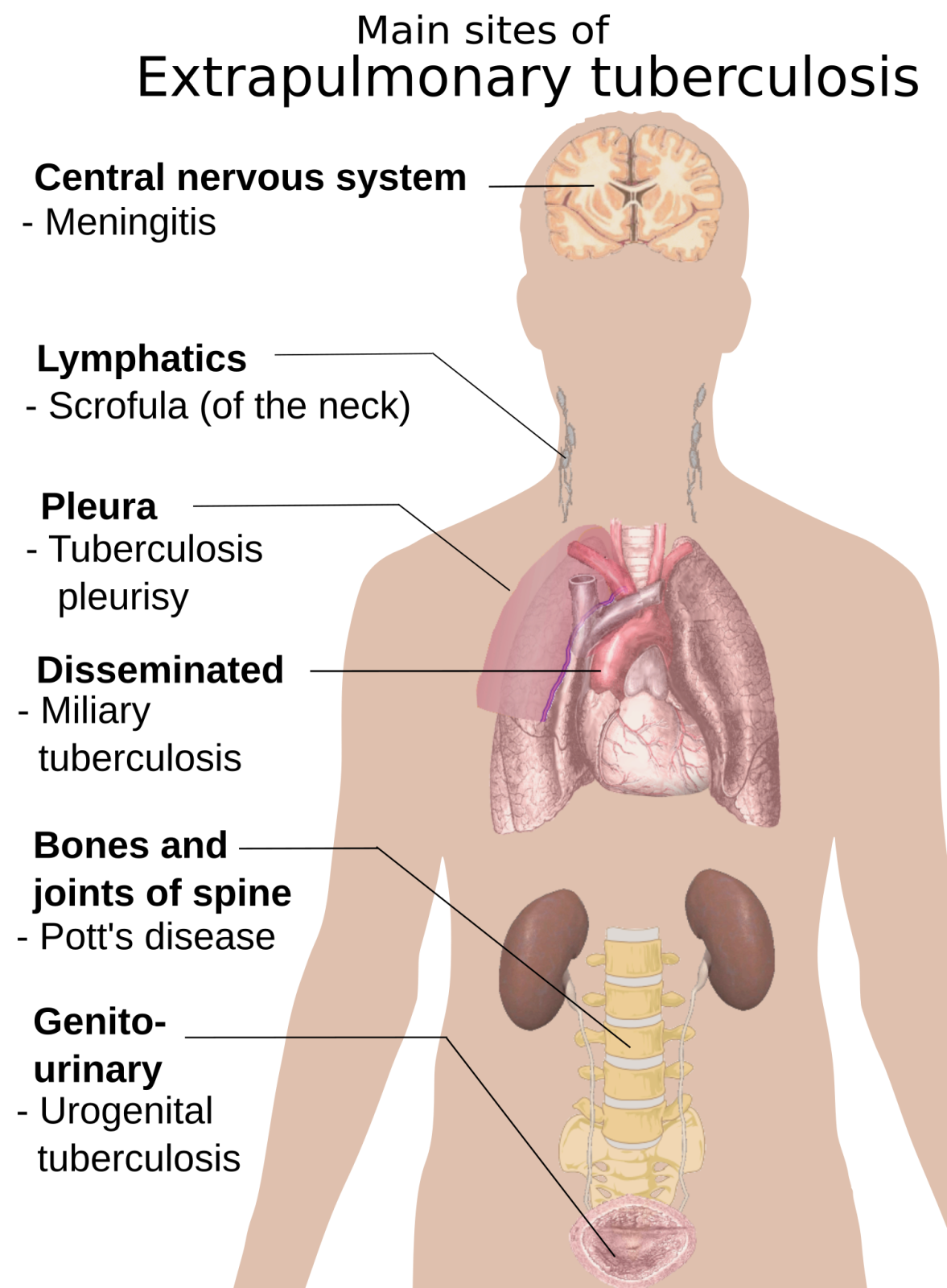
Tuberculosis (TB) is commonly associated with lung infection (pulmonary TB), but the disease can also affect other parts of the body, leading to extrapulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB). This form of TB occurs when Mycobacterium tuberculosis spreads beyond the lungs through the bloodstream or lymphatic system, affecting organs such as the brain, kidneys, spine, and lymph nodes.
Extrapulmonary TB can be harder to diagnose due to its varied symptoms, which depend on the affected organ. However, TB patients can recover fully with timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and comprehensive health insurance coverage.
This article explores the signs, tuberculosis symptoms, and treatment of extrapulmonary TB, along with the role of the best medical insurance in India in covering medical costs.
While pulmonary TB affects the lungs and respiratory system, extrapulmonary TB targets other organs and tissues. It accounts for 15-20% of all TB cases and is more common in individuals with weakened immunity, such as those with HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or malnutrition.
Unlike pulmonary TB, extrapulmonary TB is not contagious unless it affects the throat or larynx, as the bacteria are not expelled through coughing or sneezing.
Certain groups of people have a higher risk of developing EPTB, including:
People with weakened immune systems (HIV/AIDS, cancer, diabetes).
Elderly individuals with compromised immunity.
Malnourished individuals with vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
People living in crowded conditions (prisons, slums, refugee camps).
Organ transplant recipients on immunosuppressive drugs.
Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and permanent organ damage.
Extrapulmonary TB can affect various organs, leading to distinct symptoms based on the site of infection.
This is the most common form of extrapulmonary TB, particularly in children and young adults. It affects the lymph nodes, usually in the neck, underarms, and groin.
Swollen, painless lymph nodes that may enlarge over time.
Fever and night sweats.
Weight loss and fatigue.
Nodes may eventually rupture and drain pus.
Bone TB is slow-progressing and primarily affects the spine, hips, and knees. If untreated, it can cause severe deformities and disability.
Chronic back pain (spinal TB or Pott’s disease).
Joint stiffness and swelling.
Reduced mobility and bone deformities.
Neurological issues (if spinal cord compression occurs).
TB can infect the stomach, intestines, liver, spleen, and peritoneum, mimicking other digestive disorders.
Severe abdominal pain and bloating.
Persistent diarrhoea or constipation.
Loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss.
Fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites).
TB affecting the brain and spinal cord is life-threatening and requires immediate treatment.
Severe headaches and neck stiffness.
Blurred vision and sensitivity to light.
Confusion, seizures, and difficulty concentrating.
Coma in severe cases.
Kidney TB often resembles urinary tract infections (UTIs) but is more severe and persistent.
Frequent urination and painful urination.
Blood in urine (haematuria).
Lower back pain and kidney dysfunction.
High fever and night sweats.
Hepatic TB affects the liver, leading to symptoms similar to hepatitis or liver disease.
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
Liver enlargement and tenderness.
Nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
This rare but serious condition causes fluid accumulation around the heart, leading to pericarditis.
Chest pain and shortness of breath.
Swelling in legs and abdomen.
Rapid heartbeat and low blood pressure.
Since EPTB does not always affect the lungs, standard TB tests like chest X-rays may not detect the disease. Diagnosis requires:
Biopsy of infected tissue (lymph nodes, bones, or organs).
MRI or CT scan for brain, spine, or abdominal TB.
Ultrasound for kidney or liver TB.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) for TB meningitis.
Urine or blood tests to check TB bacteria presence.
Timely diagnosis ensures early intervention and better recovery outcomes.
Extrapulmonary TB is treated with a 6-12 month antibiotic regimen, similar to pulmonary TB. First-line drugs include:
Isoniazid (INH)
Rifampicin (RIF)
Pyrazinamide (PZA)
Ethambutol (EMB)
For severe cases, the treatment duration may extend to 18-24 months.
Corticosteroids like prednisolone are prescribed in cases of TB meningitis, pericardial TB, or severe inflammation.
In advanced TB, surgical intervention may be required to:
Drain abscesses in lymph nodes or abdomen.
Remove damaged bone or joint tissue.
Correct spinal deformities caused by TB.
Treating extrapulmonary TB involves long-term medications, frequent hospital visits, and advanced diagnostics, leading to high medical expenses. Having the best mediclaim policy for family ensures financial security and access to quality healthcare.
Covers diagnostic tests, hospitalisation, and medications.
Provides cashless treatment at network hospitals.
Includes critical illness insurance for severe TB complications.
Offers long-term treatment support.
Niva Bupa Health Insurance provides comprehensive medical insurance plans, ensuring hassle-free TB treatment without financial strain.
Extrapulmonary tuberculosis is a serious but treatable condition if diagnosed early. However, since its symptoms often mimic other diseases, timely medical intervention is essential for preventing complications. Persistent swelling, unexplained fever, abdominal pain, or chronic back pain could be warning signs of TB outside the lungs, requiring immediate screening and treatment.
Managing extrapulmonary TB involves long-term medication, regular monitoring, and lifestyle modifications to support recovery. Given the extended treatment duration, having financial security through the best medical insurance in India is crucial. A comprehensive health insurance policy, such as those offered by Niva Bupa Health Insurance, provides coverage for hospitalization, diagnostics, and long-term treatment, reducing financial stress during recovery.
For families looking for a safety net against unexpected medical expenses, investing in the best mediclaim policy for family ensures wide-ranging coverage, including TB treatment, specialist consultations, and post-treatment care. With the right health insurance support, TB patients can focus on recovery without financial worries and regain their normal health efficiently. If you or a loved one experiences persistent symptoms, consult a doctor immediately for early screening and medical care.

