Notifications
7 minutes, 15 seconds
-38 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews

Understanding Flange Connections: Sealing Principles, Influencing Factors, and Maintenance Best Practices
Leading Chinese Wheel Excavator Manufacturer Provides High-Quality Mini Wheeled Excavators, Construction Machinery, and Versatile Attachments.
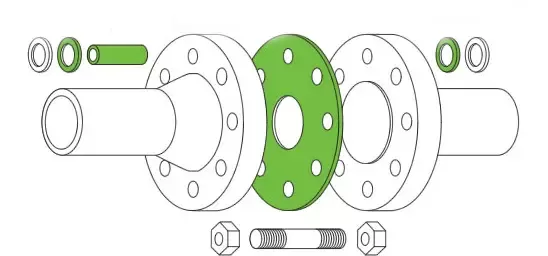
In industrial applications, flange connections are one of the most commonly used methods for joining pipelines, valves, and various equipment. They provide reliable sealing by combining bolts, flanges, and gaskets, ensuring safe and leak-proof fluid transport within pipeline systems. This article explores the sealing mechanisms, key influencing factors, and practical maintenance tips to help professionals better utilize this vital engineering solution.
The essence of a flange connection lies in achieving a tight seal. This is primarily accomplished through the interaction between the gasket, flanges, and bolt preload.
The gasket is central to the sealing process. When bolts are tightened, they generate a compressive force that causes the gasket to deform plastically and fill micro-irregularities on the flange surface. This deformation ensures minimal leakage paths and creates a pressure-tight seal.
To maintain this seal under operating conditions, the gasket must be subjected to a minimum specific pressure. When internal pressure increases during operation, the flanges tend to separate slightly, reducing the gasket's clamping force. If this force drops below a certain effective clamping threshold, the gasket may fail—potentially resulting in leaks or gasket blowout. Thus, the applied bolt tension must always exceed the pipeline's operating pressure to ensure sealing integrity.
During continuous operation, flange surfaces may separate slightly due to system dynamics. In such cases, the elastic recovery of the gasket compensates for the separation, maintaining the seal. While plastic deformation dominates the initial sealing phase, elastic recovery becomes more critical during long-term operation.
Depending on application needs and environmental conditions, different types of flange connections are used, each with distinct features:
Flat Face Flange
Features: Simple structure, easy to manufacture.
Limitations: High bolt load, lower sealing performance.
Applications: Low-pressure systems (≤2.5 MPa); not suitable for hazardous media.
Raised Face Flange
Features: Better alignment, prevents gasket extrusion.
Advantages: Resistant to erosion and suitable for higher pressures.
Drawbacks: More difficult gasket replacement.
Tongue and Groove Flange
Features: A gasket is embedded in a groove, minimizing extrusion and media exposure.
Advantages: Excellent for high-pressure, high-sealing scenarios (e.g., toxic or flammable media).
Drawbacks: Complex design; difficult gasket replacement.
Ring Joint Flange
Features: High-precision metal-to-metal sealing using ring gaskets.
Advantages: Ideal for high-pressure, high-temperature environments.
Drawbacks: Requires high machining accuracy.
Flange sealing performance is influenced by multiple variables, including:
Operating Conditions
Pressure, temperature, and media composition all affect gasket behavior.
Repeated temperature fluctuations can significantly increase leakage risk.
Gasket Properties and Specific Pressure
Gasket width, material, preload, flange surface finish, and medium characteristics all impact sealing.
Since standardized values are lacking, engineers must tailor gasket selection to each application.
Bolt Preload
Proper preload enhances sealing, but excessive force may damage the gasket or flange.
Balance is key: ensure elasticity without over-compression.
Gasket Material
The material dictates the degree of plastic and elastic deformation.
Choosing the right material is essential for performance and longevity.
Flange Stiffness and Surface Quality
Inadequate stiffness can lead to deformation and seal failure.
Ensure flange flatness, proper surface finish, and alignment during installation.
Flange leakage usually occurs via two main routes:
Gasket Permeation (rare with modern materials).
Seepage Between Gasket and Flange Surface (most common).
If the flange maintains leakage below a defined threshold under specified conditions, it is considered "tight." Otherwise, it is classified as leaking.
In operation, flanges experience complex stresses from bolts, gaskets, and internal pressure. While these forces typically don't exceed material strength limits, they can cause deformation, leading to leaks. Thus, flange designs must address both strength and stiffness to maintain seal integrity.
Correct bolt tightening sequences—typically a cross-pattern in multiple stages—are essential to distribute clamping force evenly and prevent flange warping or localized leakage.
Routine maintenance is critical for extending the service life and ensuring the reliability of flange connections. Recommended practices include:
Bolt Tension Checks
Temperature changes and vibrations can loosen bolts. Inspect and retighten as needed to maintain proper preload.
Gasket Condition Monitoring
Replace gaskets showing signs of wear, aging, or deformation to maintain sealing effectiveness.
Surface Cleanliness and Flatness
Ensure flange faces are clean and undamaged; flatness is vital for uniform gasket compression.
Deformation Inspection
Check for warping or mechanical damage that can impair sealing.
Operating Condition Monitoring
Track pressure, temperature, and medium changes. Adjust sealing systems accordingly.
Flange connections are a cornerstone of safe and reliable industrial piping systems. They rely on a careful balance of bolt preload, gasket behavior, and flange design to maintain a seal under challenging conditions. Understanding the mechanical principles, selection criteria, and maintenance routines is essential for engineers and operators aiming to reduce leakage risks and maximize operational efficiency.
By selecting the right flange type, using appropriate gasket materials, and maintaining correct bolt tension, we can ensure long-term sealing performance. Regular inspection and proactive maintenance are crucial for preventing system failures and reducing downtime in critical industrial operations.Know more about Google SEO Directory
Wheel Excavator Manufacturer China Excavator Manufacturer China Wheeled Excavators

