Notifications
8 minutes, 13 seconds
-48 Views 0 Comments 0 Likes 0 Reviews

Pollution of water through sewage processing plants is a critical issue in the fast-developing, urbanized world. Untreated sewage causes extreme environmental degradation, which impacts water bodies, soil, and air quality. Appropriate sewage treatment not only protects the environment but also improves the health and well-being of people.
This article explores how sewage processing plants (STPs) play a crucial role in reducing pollution, their benefits, and the latest technological innovations driving sustainable water management.
Sewage refers to wastewater generated from households, industries, and stormwater runoff. It typically contains organic matter, chemicals, pathogens, and suspended solids.
Domestic sewage: Home wastewater (kitchen, bathroom, laundry).
Industrial sewage: Waste from manufacturing and processing industries.
Stormwater runoff: Rainwater that carries pollutants on the streets and surfaces.
Untreated sewage leads to:
Water contamination, which is detrimental to aquatic organisms.
Pollution of soil, rendering it infertile.
Air pollution from harmful gases such as methane and hydrogen sulfide.
Over 80% of wastewater worldwide is discharged untreated.
According to the UN, over 2 billion people drink water contaminated with sewage, contributing to disease outbreaks.
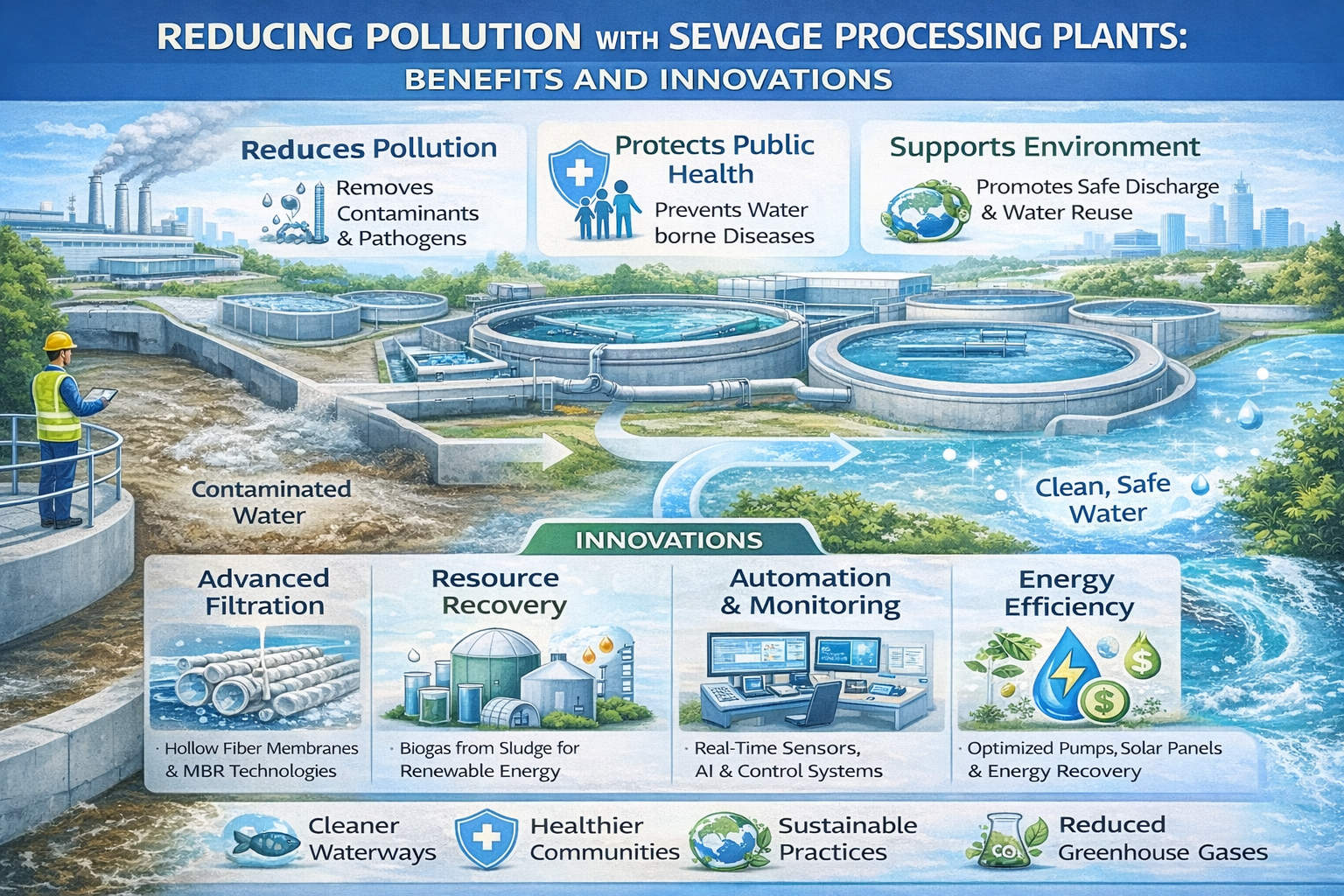
Sewage Processing Plants (STPs)are wastewater treatment facilities used to treat wastewater prior to its discharge into the environment. They are meant to eliminate pollutants and pathogens in order to render water safe for reuse or discharge.
Primary treatment: This is the first step of treatment whereby the water is taken through screens to eliminate large objects such as plastics and sticks. Then it is placed in tanks where dirt and solid masses settle at the bottom.
Secondary treatment: The second step is a process whereby microorganisms such as bacteria digest the remaining waste in the water, making it significantly cleaner.
Tertiary treatment: The last stage is the filtration and disinfection of the water to eliminate germs and small contaminants. Once this is done, the water should be reused or discharged into rivers.
Screening units
Sedimentation tanks
Biological reactors
Filtration systems
Disinfection units
Sewage facilities are used to make our environment clean. They filter contaminated water, which is then released into rivers and lakes, thereby protecting fish and plants. They also prevent the entry of harmful chemicals in soil and underground water.They also eliminate unpleasant odors and toxic gases in the air.
People remain healthy because of sewage plants. These plants reduce the risk of such diseases as cholera and dysentery because of clean water. They also ensure that towns and villages are clean hence everyone can live in a safer and healthier place.
Sewage facilities conserve funds and resources. Farms or factories can reuse clean water. Waste in the plants can be converted to energy or fertilizer. These plants save organizations from expenses of environmental cleaning and treatment of the ill through reduction of pollution.
The process of microfiltration, ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis are processes that behave as very fine sieves to remove tiny particles, bacteria and harmful materials in water.
They render wastewater much cleaner and usable.
Anaerobic digestion refers to the process of decomposing sewage sludge in the absence of oxygen by bacteria to generate biogas which can be utilized as energy.
Solar-powered treatment plants utilize the sunlight to energize machines and pumps, which conserve electricity and lessen pollution caused by using energy.
Real-time water quality monitoring entails the use of sensors that continuously measure water to ensure that it is clean.
Predictive maintenance involves information on sensors to repair issues before they develop as serious problems and helps save time and costs.
Sewage should not be treated only as waste, it can be used to produce fertilizers, energy, recycled water which could be used in the farming industry or household.
These systems together with the city water management are beneficial in enabling cities to utilize their resources effectively and remain environmentally friendly.
Singapore has constructed modern water treatment plants which have the capability of purifying wastewater to a level that approximately 40 % can be re-used as drinking water. This will assist the city to save water and preserve the environment.
Sweden is one of those countries that treat sewage to generate biogas. Buses and industries are then powered using this biogas, thus making sewage a useful source of energy and eliminating pollution.
Local sewage treatment plants in Pune, India have assisted in cleaning rivers. Within five years, these plants had cut down on water pollution by over 60% making the waters safe for people and animals.
Challenges:
The initial installations and maintenance are expensive.
There is a need for qualified operators and technology.
Future prospects:
Smart sewage management AI and IoT.
Energy efficient and zero waste innovations.
To avert pollution associated with the sewage processing plants is not only an environmental imperative but a motivating factor towards population health, economic effectiveness and sustainable use of resources. Firms such as OXYMO TECHNOLOGY are leading the new technologies in sewage treatment, and it is now simple to have the community invest in clean water projects and a healthy future.
Q. What are the functions of sewage treatment plants?
They remove untreated domestic and industrial water to make it safe to humans, animals and the environment.
Q. What do sewage plants do to make people healthy?
They prevent such diseases as cholera and typhoid by eliminating germs and bacteria.
Q. Is it possible to reuse treated sewage water?
Yes. Watering plants, toilet flushing or farming can be done using clean water.
Q. Are sewage plants beneficial to the environment?
Yes. They prevent pollution of rivers, lakes and soil and they preserve fish and plants and clean water.

